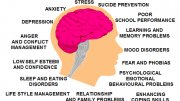
Common distractions are: anxiety, mistakes, fatigue, weather, public announcements, coach, manager, opponent, negative thoughts etc.
Strategies to improve concentration are very personal. One way to maintain focus is to set process goals for each session or competition. The athlete will have an overall goal for which the athlete will identify a number of process goals that help focus on specific aspects of the task. For each of these goals the athlete can use a trigger word (a word which instantly refocuses the athlete's concentration to the goal) e.g. sprinting technique requires the athlete to focus on being tall, relaxed, smooth and to drive with the elbows - trigger word could be "technique"
Athletes will develop a routine for competition that may include the night before, the morning, pre competition, competition and post competition routines. If these routines are appropriately structured then they can prove a useful aid to concentration.
Confidence
When an athlete has self confidence they will tend to: persevere even when things are not going to plan, show enthusiasm, be positive in their approach and take their share of the responsibility in success and fail.
- visualise previous good performance to remind them of the look and feel
- imagine various scenarios and how they will cope with them
Good goal setting (challenging yet realistic) can bring feelings of success. If athletes can see that they are achieving their short term goals and moving towards their long term goals then confidence grows.
Confidence is a positive state of mind and a belief that you can meet the challenge ahead - a feeling of being in control. It is not the situation that directly affects confidence; thoughts, assumptions and expectations can build or destroy confidence.
High self confidence
- Thoughts - positive thoughts of success
- Feelings - excited, anticipation, calm, elation, prepared
- Focus - on self, on the task
- Behaviour - give maximum effort and commitment, willing to take chances, positive reaction to set backs, open to learning, take responsibility for outcomes
Low self confidence
- Thoughts - negative, defeat or failure, doubt
- Feelings - tense, dread, fear. not wanting to take part
- Focus - on others, on less relevant factors (coach, umpire, conditions)
- Behaviour - lack of effort, likely to give up, unwilling to take risks (rather play safe), blame others or conditions for outcome
Source: www.brianmac.co.uk
You might also like: